题目
解析
用stack记录出现过的括号, 遇到左括号就入栈括号的位置; 遇到右括号时, 若栈不为空则可构成合法括号, 出栈一个元素; 否则将当前位值标注为待删除. 最后将栈内剩余元素(没有右括号可以匹配的左括号)全部标记待删除. 最后调用string::erase()方法或其他语言的类似方法一次全部删除.
代码
c++
1 | class Solution { |
用stack记录出现过的括号, 遇到左括号就入栈括号的位置; 遇到右括号时, 若栈不为空则可构成合法括号, 出栈一个元素; 否则将当前位值标注为待删除. 最后将栈内剩余元素(没有右括号可以匹配的左括号)全部标记待删除. 最后调用string::erase()方法或其他语言的类似方法一次全部删除.
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
从最宽的开始, 如果比它窄的箱子想装更多水, 就一定要比它高.
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
将power 和 index 组成 pair 放入set(set会自己排好序), 然后返回k个index就好.
1 | class Solution { |
用dfs解题TLE了, 查了一下并查集的解法, 通过了. 链接在此
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class DisjointSet { |
In an N by N square grid, each cell is either empty (0) or blocked (1).
A clear path from top-left to bottom-right has length k if and only if it is composed of cells C_1, C_2, ..., C_k such that:
C_i and C_{i+1} are connected 8-directionally (ie., they are different and share an edge or corner)C_1 is at location (0, 0) (ie. has value grid[0][0])C_k is at location (N-1, N-1) (ie. has value grid[N-1][N-1])C_i is located at (r, c), then grid[r][c] is empty (ie. grid[r][c] == 0).Example 1:
Input: [[0,1],[1,0]]
Output: 2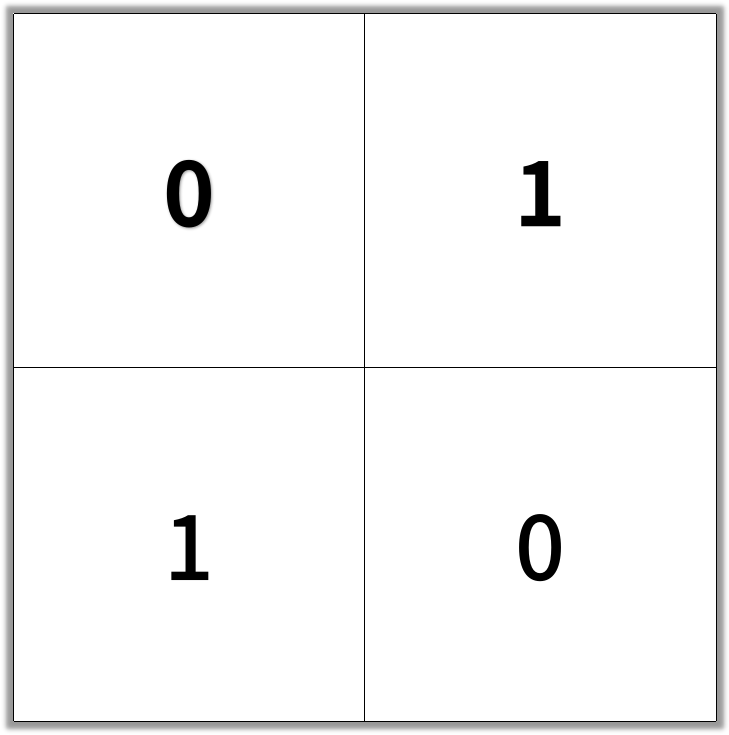
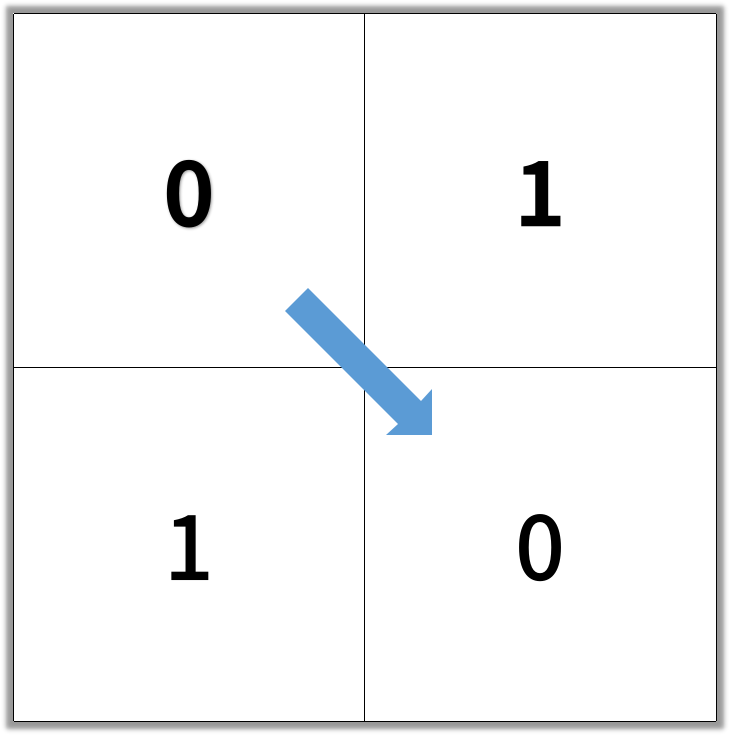
Example 2:
Input: [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
Output: 4

Note:
1 <= grid.length == grid[0].length <= 100grid[r][c] is 0 or 1典型的BFS算法, 用queue维护待搜索节点, 搜索过的节点要标注以避免死循环.
1 | class Solution { |
Given a non-negative integer num, return the number of steps to reduce it to zero. If the current number is even, you have to divide it by 2, otherwise, you have to subtract 1 from it.
Example 1:
Input: num = 14
Output: 6
Explanation:
Step 1) 14 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 7.
Step 2) 7 is odd; subtract 1 and obtain 6.
Step 3) 6 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 3.
Step 4) 3 is odd; subtract 1 and obtain 2.
Step 5) 2 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 1.
Step 6) 1 is odd; subtract 1 and obtain 0.
Example 2:
Input: num = 8
Output: 4
Explanation:
Step 1) 8 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 4.
Step 2) 4 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 2.
Step 3) 2 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 1.
Step 4) 1 is odd; subtract 1 and obtain 0.
Example 3:
Input: num = 123
Output: 12
Constraints:
0 <= num <= $10^6$
遍历bits, leading zeros 不算, 其余位是1就加2, 是0就加1.
1 |
Given two strings s and t , write a function to determine if t is an anagram of s.
Example 1:
Input: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram"
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: s = "rat", t = "car"
Output: false
Note:
You may assume the string contains only lowercase alphabets.
Follow up:
What if the inputs contain unicode characters? How would you adapt your solution to such case?
统计每个字符的出现次数加入set, 然后比较两set是否相等. 因为输入只包含小写字母, 可用int[26]代替.
py可以直接调用Counter.
1 | class Solution(object): |
1 | class Solution { |
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representing Node.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from 0 to n-1) that the random pointer points to, or null if it does not point to any node.Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1: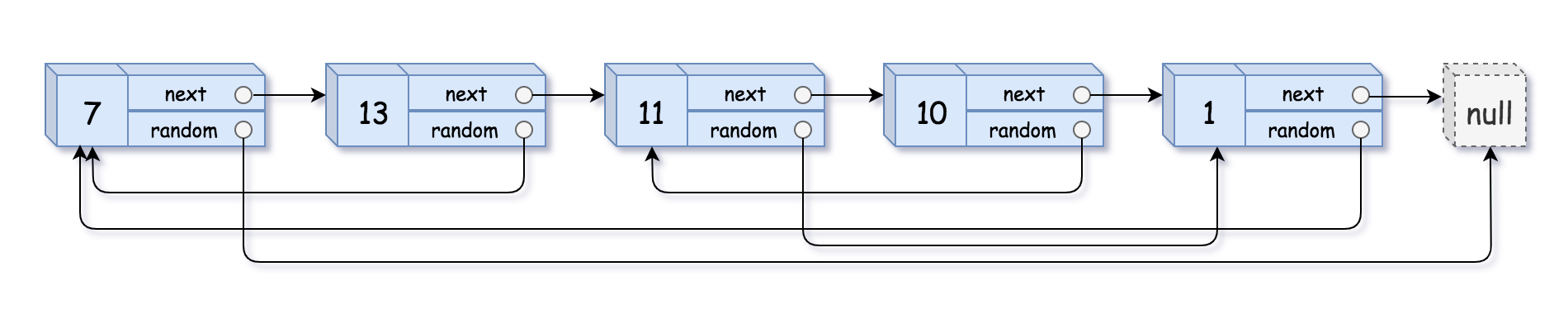
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2: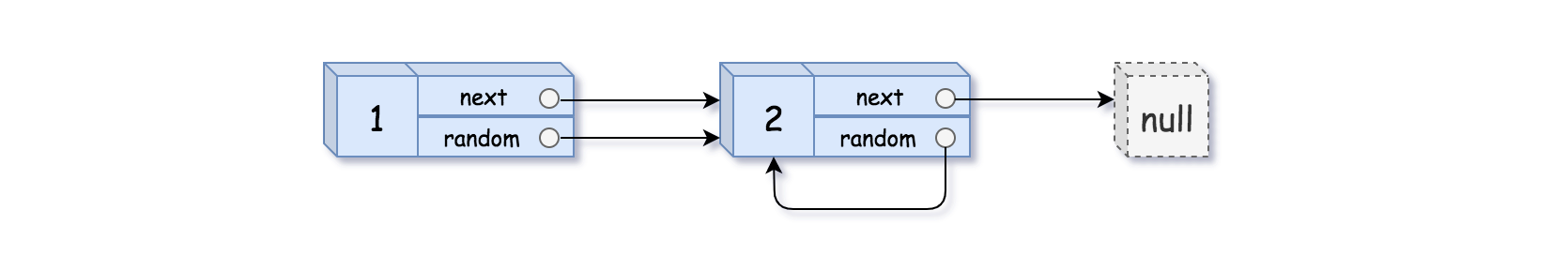
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3: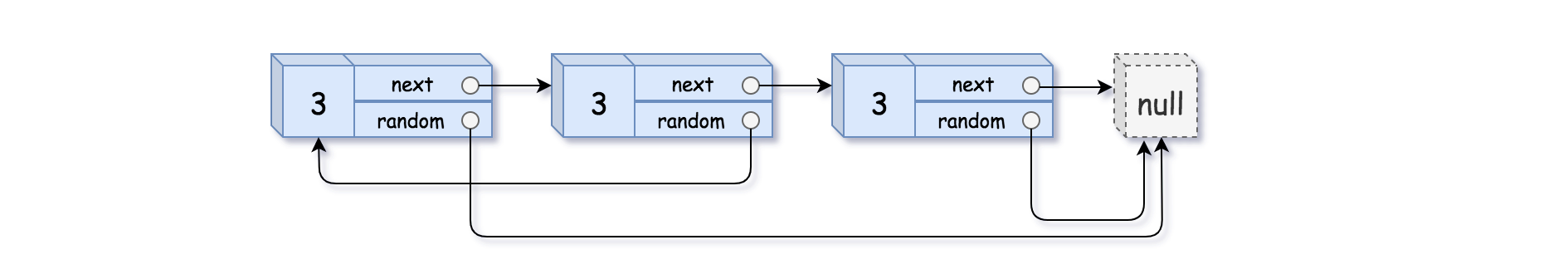
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Example 4:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Explanation: The given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 1000-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.random is null or is pointing to some node in the linked list.